Ectopic Pregnancy: A Complete Patient Guide for Early Detection and Safe Recovery
Imagine this: You’ve just found out you’re pregnant—maybe it’s your first time, or maybe it’s been a long-awaited moment. But instead of the joyful journey you envisioned, you’re suddenly faced with unexpected pain, bleeding, or even a diagnosis that you may have never heard of before—ectopic pregnancy.
As a gynaecologist, I’ve seen the confusion, fear, and emotional weight this diagnosis can bring. Ectopic pregnancy affects around 1 in 90 pregnancies, and despite being relatively rare, it remains one of the leading causes of maternal death in the first trimester. This makes awareness not just helpful—but potentially life-saving.
In this complete patient guide, I’ll help you understand what ectopic pregnancy is, why it can’t continue, the symptoms to watch for, causes, diagnosis methods, and your treatment options. Whether you’re trying to conceive or simply want to be informed, this article is here to guide you with facts, clarity, and compassion.
Also Read:
- Hysteroscopy in India: Finding the Right Care and What to Ask Your Doctor
- Recognising the Warning Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy Early
- Ectopic Pregnancy and Fertility: A Guide to Healing, Hope, and Trying Again
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy and Why It Cannot Continue
An ectopic pregnancy is a potentially life-threatening condition in early pregnancy, where a fertilised egg implants outside the uterus—most often in the fallopian tube. This is why it’s commonly referred to as a tubal pregnancy. In rare cases, the egg may implant in the ovary, cervix, abdominal cavity, or within a Caesarean scar.
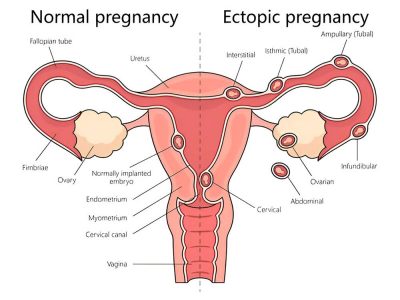 Why Ectopic Sites Cannot Support a Pregnancy
Why Ectopic Sites Cannot Support a Pregnancy
In a typical pregnancy, the fertilised egg moves through the fallopian tube and attaches itself securely to the lining of the uterus, where it can grow and develop. But the fallopian tubes and other ectopic locations cannot expand or nourish a developing embryo. These areas lack the support systems—like thick muscular walls and rich blood supply—needed for foetal growth.
As the pregnancy tissue enlarges, it begins to stretch and damage these fragile structures, often leading to rupture and life-threatening internal bleeding.
⚠️ Why Ectopic Pregnancy Is Non-Viable:
- A fertilised egg cannot survive outside the uterus
- Locations like the fallopian tube or ovary lack the space and blood supply needed for development
- As the embryo grows, it can cause the surrounding tissue to rupture, leading to severe internal bleeding
- Immediate medical treatment is critical to avoid life-threatening complications
For these reasons, pregnancy cannot progress to term and requires prompt diagnosis and intervention to protect your health. In the next section, we’ll explore how to spot early symptoms of ectopic pregnancy and when to seek urgent care.
Signs and Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
The signs of an ectopic pregnancy often mimic a normal pregnancy in its early stages, which can delay diagnosis. Being aware of key symptoms helps in recognising the condition before complications develop.
Typical symptoms include:
- Sharp or stabbing abdominal or pelvic pain, often on one side
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting different from a period
- Pain during urination or bowel movements
- Persistent lower back discomfort
- Shoulder tip pain, which may signal internal bleeding
- Lightheadedness, fainting, or general weakness
Many women overlook early warning signs, assuming symptoms are normal. Megan, a patient who faced recurrent pregnancy loss, shares how recognising her symptoms—and trusting her instincts—became lifesaving.
I had lost a fallopian tube, battled miscarriages, and thought it was finally my turn. But ectopic pregnancy doesn’t wait for hope. You have to know the signs, trust your body, and speak up- Megan
Shoulder tip pain, in particular, is a red flag—it can indicate blood irritating the diaphragm, a sign of internal bleeding. Any combination of these symptoms, especially if pregnancy is confirmed, should prompt immediate medical evaluation.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ectopic Pregnancy
Knowing what increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy can help women stay proactive about early signs and medical screening. While it can happen to anyone, certain medical histories and lifestyle choices raise the risk.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy are often linked to:
- Blockage or damage in the fallopian tubes due to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- Tubal surgery or abdominal procedures
- Fertility treatments such as IVF
- Endometriosis, which causes scarring and inflammation
- Smoking, which alters tubal function
- Pregnancy with an IUD in place carries a higher risk of being ectopic/
- Maternal age over 35
Being aware of these risk factors allows for early testing, monitoring, and informed medical discussions, especially for women undergoing fertility treatments or those with a history of reproductive issues.
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
Timely and accurate diagnosis plays a vital role in reducing the risk of serious complications associated with ectopic pregnancy. Since ectopic pregnancy symptoms can be vague, diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical and lab-based evaluations.
 Doctors typically perform:
Doctors typically perform:
Transvaginal Ultrasound and Pelvic Exam
A transvaginal ultrasound helps locate the pregnancy and check for the presence or absence of a gestational sac in the uterus. If a sac isn’t visible at expected hCG levels, ectopic pregnancy is suspected.
A pelvic examination may also detect signs such as tenderness, swelling, or the presence of a mass near the fallopian tube.
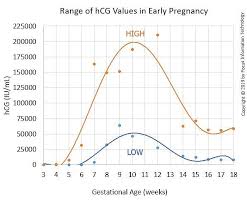
Serial hCG Blood Tests
In a healthy pregnancy, hCG levels should double every 48–72 hours. In cases of ectopic pregnancy, hCG levels typically rise more slowly or follow an irregular pattern, unlike the steady increase seen in a healthy intrauterine pregnancy.
An ectopic pregnancy should be suspected when a transvaginal ultrasound reveals no intrauterine gestational sac, despite β-hCG levels exceeding 1,500 mIU/mL.
 Additional tools like serum progesterone, diagnostic laparoscopy, or uterine aspiration may be used to confirm or rule out ectopic pregnancy.
Additional tools like serum progesterone, diagnostic laparoscopy, or uterine aspiration may be used to confirm or rule out ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
The treatment approach depends on how early the ectopic pregnancy is detected, whether it has ruptured, and the patient’s overall condition. The three main methods include medication, surgery, and careful observation.
Medical Management with Methotrexate
Methotrexate is a first-line, non-surgical treatment for unruptured ectopic pregnancy. This drug halts cell growth, allowing the body to absorb the tissue naturally. It’s administered by injection and requires follow-up hCG monitoring.
Women must avoid alcohol, folic acid, and physical exertion during treatment. Pregnancy should be avoided for at least three months post-treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is required if the pregnancy has ruptured or if methotrexate isn’t suitable. The most common procedure is laparoscopy, which removes the ectopic tissue through small incisions.
- If the fallopian tube is extensively damaged or ruptured, a salpingectomy—the surgical removal of the affected tube—may be necessary to prevent further complications.
- In emergency situations, an open surgical procedure known as laparotomy may be required, especially when there is heavy internal bleeding or the patient is unstable.
Expectant Management
Rarely, if hCG levels are falling and the patient is stable, doctors may opt for watchful waiting. This requires regular monitoring to ensure the tissue is resolving naturally. It’s only suitable when no immediate risk is present.
Recovery and Emotional Support After Ectopic Pregnancy
Physical healing is only part of the recovery. Many women experience emotional stress, grief, or anxiety. A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting physical recovery and restoring strength.
Physical Recovery
Recovery after surgery or methotrexate may take a few weeks. Some discomfort and fatigue are normal. Regular follow-up appointments and blood tests are important to ensure full resolution.
Emotional Healing
A pregnancy is a loss. It’s natural to feel grief, fear about future pregnancies, or depression. Speaking with a therapist, joining support groups, or leaning on loved ones can be healing.
Support organisations such as the Ectopic Pregnancy Trust provide valuable resources, guidance, and emotional support for the recovering individuals.
 Future Fertility
Future Fertility
Many women can conceive again after an ectopic pregnancy, even if one fallopian tube was removed. However, the risk of recurrence is around 10% after one episode. Future pregnancies should be closely monitored early on with serial hCG and early ultrasound to rule out recurrence.
Restoring hormonal balance is an important part of the healing process after an ectopic pregnancy, as the body gradually adjusts to changing hormone levels.
Also Read:
- Women’s Health After 40: What Changes and How to Stay Ahead
- Recognising the Warning Signs of Ectopic Pregnancy Early
Conclusion: Act Early, Stay Informed
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition, but with timely intervention, most women recover fully. Being aware of ectopic pregnancy symptoms. Important to know the risk factors. Always seeking immediate care can prevent complications and protect your fertility.
If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy or experience unusual symptoms in early pregnancy, don’t delay. Early action can save lives—and futures.
Our Digital Imprints:
Dr. Madhu Goel
Senior Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
Director, Fortis La Femme
I am passionate about women’s health. With expertise in managing high-risk pregnancies, infertility, and various gynaecological issues, I strive to provide compassionate care. I am committed to ensuring the well-being of my patients. Follow me for insights and updates on women’s health.
Connect to my Newsletter
“Health Hub”: Women’s Health & Wellness
Connect with me: Instagram | Facebook | LinkedIn



