Cervical Cancer & HPV Vaccine: What Every Woman Must Know
Cervical cancer in India, is one of the leading cancers among Indian women, taking a life every seven minutes. The HPV vaccine in India offers a powerful tool to change this reality.
Targeting the human papillomavirus (HPV) — the leading cause of cervical cancer — vaccination can prevent thousands of cases each year. With affordable options like Cervavac now available, prevention is more accessible than ever. This article explains everything you need to know about cervical cancer, the vaccine, eligibility, schedule, costs, safety, and common myths.
Whether you are a parent, a young woman, or simply an advocate for women’s health, understanding your options is the first step toward protection. Cervical cancer is largely preventable. HPV vaccine is one of the most effective ways to safeguard your future health. Empowered women can take care of their health and well-being.
Also Read:
- Cervical Cancer Screening: What Test is Right for You?
- Cervical Screening After Vaccination: Why It Still Matters
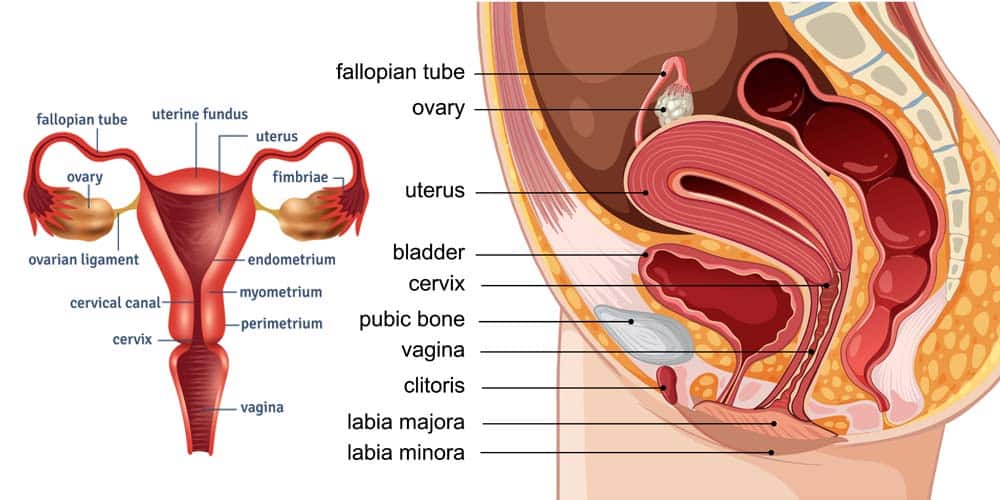
Understanding Cervical Cancer and HPV
Cervical cancer develops in the cells lining the cervix, often as a result of persistent infection with high-risk HPV strains. HPV types 16 and 18 are responsible for about 70% of cases, highlighting the strong HPV and cervical cancer link.
The virus spreads through intimate skin-to-skin contact. Most HPV infections resolve on their own, but some linger and lead to abnormal cell changes that may develop into cancer.
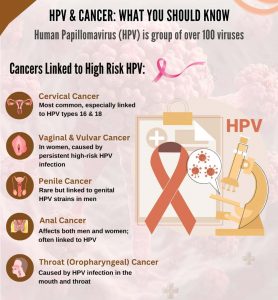
HPV can also cause:
- Cervical cancer – most common in women
- Vaginal and vulvar cancers
- Penile cancer in men
- Anal cancer in both genders
- Certain throat cancers (HPV-related cancers)
 Low-risk HPV types 6 and 11 cause nearly 90% of genital warts but are not linked to cancer. Understanding this link is crucial because it makes prevention possible. Regular screening and vaccination against HPV can significantly lower your risk. Cervical cancer does not have to be a leading cause of death — with awareness and prevention, we can change the statistics.
Low-risk HPV types 6 and 11 cause nearly 90% of genital warts but are not linked to cancer. Understanding this link is crucial because it makes prevention possible. Regular screening and vaccination against HPV can significantly lower your risk. Cervical cancer does not have to be a leading cause of death — with awareness and prevention, we can change the statistics.
HPV Vaccine – A Key to Prevention
The human papillomavirus vaccine is a preventive measure, not a treatment. It uses virus-like particles (VLPs) — harmless protein shells that mimic HPV — to train the immune system without causing disease. Once vaccinated, your body produces antibodies that can block infection if exposed later.
 Clinical studies reveal that the cervical cancer vaccine can prevent up to 90% of cases if administered before exposure. Protection lasts at least 12 years, and no booster is currently recommended. The vaccine also supports herd immunity, indirectly protecting unvaccinated individuals by reducing virus circulation.
Clinical studies reveal that the cervical cancer vaccine can prevent up to 90% of cases if administered before exposure. Protection lasts at least 12 years, and no booster is currently recommended. The vaccine also supports herd immunity, indirectly protecting unvaccinated individuals by reducing virus circulation.
Key benefits of the HPV vaccine:
- Prevents most HPV-related cancers
- Protects against genital warts
- Offers long-term immunity
- Supports community-wide protection
Addressing HPV vaccine myths is essential — it does not cause infertility, and it’s not only for women. In fact, vaccinating boys reduces virus spread and benefits everyone. The HPV vaccine is a safe, proven shield against a major cancer threat.
Who Should Get Vaccinated (Eligibility)
The HPV vaccine eligibility guidelines prioritise vaccinating before exposure to HPV for maximum benefit.
Recommended groups:
- Primary target: Girls aged 9–14 years (ideal window for best immune response)
- Catch-up: Females aged 15–26 years who missed earlier vaccination
- Extended: Women aged 27–45 may benefit after consulting their healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
The HPV vaccine age limit India recommendations now also include boys. HPV vaccination for boys protects them from HPV-related cancers and reduces virus transmission to partners.
Eligibility at a glance:
- 9–14 years: Strongest protection
- 15–26 years: Good protection
- 27–45 years: Case-by-case decision
https://trendvisionz.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/hpv-vaccination-schedule-india-1.jpg
If you’re unsure about your eligibility, speak with your gynaecologist. Even if you are sexually active, the vaccine can still protect you against HPV types you haven’t yet encountered.
HPV Vaccine Schedule
Following the correct HPV vaccine schedule ensures full protection.
Recommended schedules:
- Ages 9–14: Two doses, 0 and 6–12 months apart
- Ages 15–45: Three doses, 0, 1–2 months, and 6 months
- Immunocompromised: Three doses at the same intervals, any age
Recently, the WHO HPV vaccination schedule update recommended a single dose for girls under 15, based on studies showing similar effectiveness. This could make large-scale immunisation easier in India.
If a dose is missed, there’s no need to restart — just resume where you left off. Adhering to the schedule is important for long-term protection. Consult your doctor to determine the best vaccination plan for you or your child.
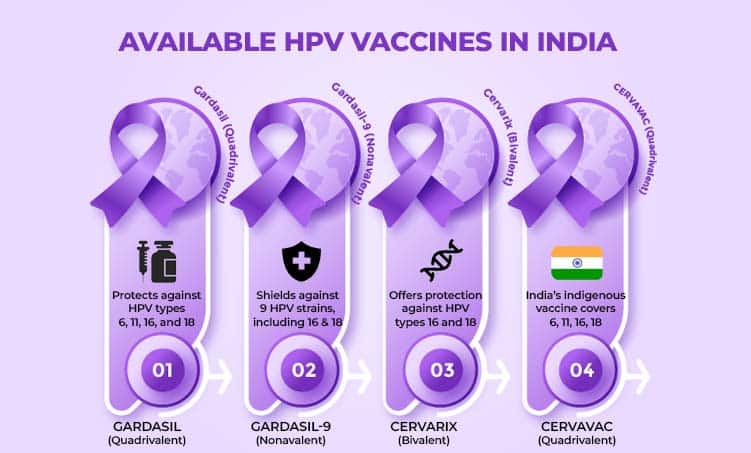
HPV Vaccine Options in India
Several vaccines are available in India, differing in HPV type coverage, age approval, and cost.
Key options:
- Gardasil 9: Protects against 9 HPV types; broadest coverage; approved for ages 9–45; approx ₹9,000–₹10,850 per dose (Gardasil 9 in India)
- Gardasil: Quadrivalent; protects against 4 types; approved for ages 9–26; approx ₹2,000–₹4,000
- Cervarix: Bivalent; targets 2 high-risk types; approved for ages 9–25; approx ₹3,000–₹3,500
- Cervavac: India’s first indigenous quadrivalent vaccine; affordable at approx ₹2,000; approved for ages 9–26 (Cervavac HPV vaccine)
When considering the HPV vaccine cost in India, balance protection level with budget. Gardasil 9 offers the widest protection but at a higher price, while Cervavac makes prevention more accessible.
Cost and Government Support
The HPV vaccine cost in India varies widely:
- Private sector: ₹2,000–₹10,850 per dose
- Government programmes: Free or heavily subsidised for eligible groups
State governments like Sikkim and Punjab have achieved coverage rates above 90% through school-based drives. Under national plans, the Cost of HPV in India could drop further with Cervavac’s inclusion in public programmes.
How to access subsidised vaccination:
- Check with your local Primary Health Centre (PHC)
- Enquire at government hospitals
- Look out for school immunisation drives
Reducing the cervical cancer burden in India requires both awareness and affordable access — government support plays a key role in reaching underserved areas.
Safety and Side Effects
The HPV vaccine safety record is strong, with over 15 years of global use. Side effects are generally mild and short-lived.
Common:
- Pain, swelling, or redness at injection site
- Mild fever, headache, tiredness
Rare:
- Fainting (prevented by resting for 15 minutes after injection)
- Severe allergic reaction (extremely rare)
HPV vaccine side effects are far less dangerous than the diseases the vaccine prevents. Contraindications include pregnancy and severe allergy to a vaccine component. Always discuss your health history with a doctor before vaccination. Alongside vaccination, maintaining good nutrition, including adequate magnesium intake, supports women’s health throughout life
 Busting Common Myths
Busting Common Myths
Misinformation fuels vaccine hesitancy. Let’s separate fact from fiction:
- ❌ Myth: HPV vaccine causes infertility
✔ Fact: No evidence; untreated HPV poses higher fertility risk - ❌ Myth: Vaccine is only for women
✔ Fact: Also for boys, prevents several HPV-related cancers - ❌ Myth: Ineffective long-term
✔ Fact: Protects for at least 12 years, no boosters needed - ❌ Myth: Not useful if sexually active
✔ Fact: Still guards against HPV types not yet contracted
Tackling HPV vaccine myths is vital to improving coverage in India.
FAQs
Q: Do vaccinated women still need cervical cancer screening?
A: Yes. The vaccine doesn’t cover all HPV types; regular screening is essential.
Q: Is the HPV vaccine safe during breastfeeding in India?
A: Yes, it is considered safe.
Tackling HPV vaccine myths is key to increasing coverage in India.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is preventable, and the HPV vaccine in India is a proven, safe, and effective way to achieve that. By combining vaccination with regular screening, we can dramatically reduce the number of cases and save lives.
Whether you’re a parent or an adult woman, take the step to protect yourself or your child. Prevention is always better than cure — and in the case of cervical cancer, it can mean the difference between life and death. Hey empowered women always stay Informed and Take proactive steps today can protect your
Talk to your healthcare provider today, check eligibility, and join the movement to eliminate this disease from India’s future.
Our Digital Imprints:
Dr. Madhu Goel
Senior Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
Director, Fortis La Femme
I am passionate about women’s health. With expertise in managing high-risk pregnancies, infertility, and various gynaecological issues, I strive to provide compassionate care. I am committed to ensuring the well-being of my patients. Follow me for insights and updates on women’s health.
Get Connected to my Newsletter
“Health Hub”: Women’s Health & Wellness
Connect with me: Instagram | Facebook | LinkedIn